Architecture Overview
High-Level Overview
Section titled “High-Level Overview”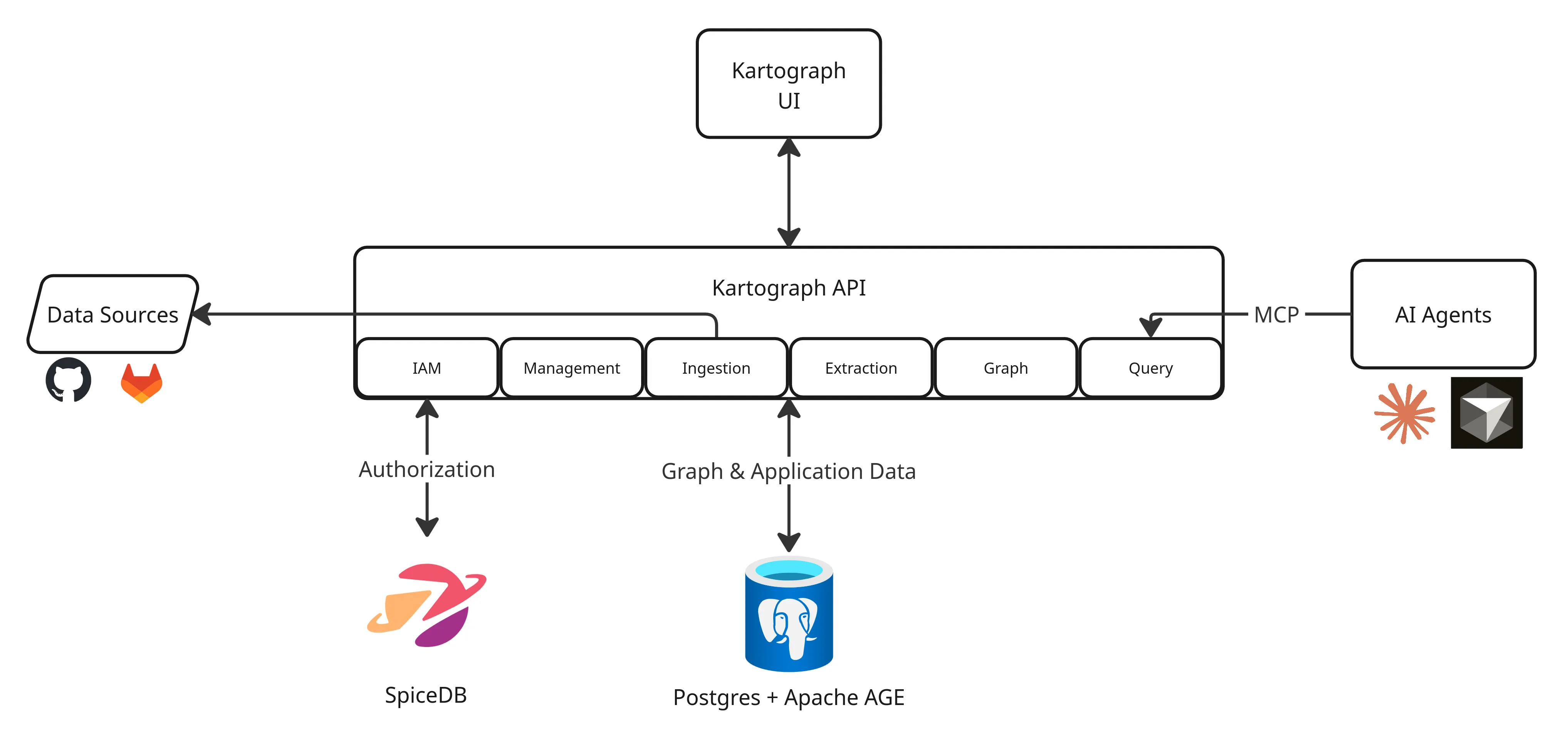
Kartograph can be described at a high level with the following components:
Kartograph UI Not Started
Section titled “Kartograph UI ”The Kartograph UI provides a low-friction interface to creating and managing knowledge graphs and the data sources that feed them.
Kartograph API
Section titled “Kartograph API”The Kartograph API, built as a modular monolith, is the engine that powers the Kartograph platform. Its functionality is best described by its six bounded contexts (also referred to as domains, see Martin Fowler on DDD to learn more.)
-
IAM In-Progress
The Identity and Access Management (IAM) domain handles authentication and authorization. Fine-grained authorization is achieved via SpiceDB.
-
Management Not Started
The management domain is responsible for handling knowledge graph and data source settings. It manages graph names, data source credentials, sync schedules, and more.
-
Ingestion Not Started
The ingestion handles the retrieval of data from data sources. It uses a pluggable adapter pattern that, in theory, allows connecting arbitrary data sources to Kartograph. In practice, every new data source type requires the creation of an adapter before it can be ingested.
The Kartograph team is committed to using its limited resources to provide adapters for the most popular data sources. We welcome contributions from the community!
-
Extraction In-Progress
The extraction domain handles the transformation of a data source into a set of entities and relationships that will make up a graph.
LLM-based agents are the core engine behind the extraction. We are actively iterating on the methodology, and are currently using the Agent SDK from Anthropic.
As of writing, the extraction domain is expected to produce a JSON lines (JSONL) file containing mutation operations (
DEFINE/CREATE/UPDATE/DELETE), which will be applied by the graph domain. -
Graph MVP
The graph domain is responsible for managing interactions with the knowledge graphs. It takes the JSONL produced by the extraction domain and applies the changes to a graph.
An abstract protocol is used at the infrastructure layer of the graph domain such that, in theory, Kartograph can support any graph database backend. In practice, we only provide support for the Postgres extension Apache AGE.
-
Query MVP
The query domain is the “front door” to graph data for AI agents (or other consumers). At this time, the query domain exposes a model context protocol (MCP) that provides a tool and several resources that enable agents to execute openCypher queries.
To learn more, see the MCP Sever Guide.
Typical User Journey
Section titled “Typical User Journey”The following contrived user story helps to illustrate the intended user journey.
Let’s assume that Alice and Bob are members of a team named Catalyst that wants to build a knowledge graph from three of their GitHub repos.
- Bob opens the Kartograph UI and creates a new team called “Catalyst”, and adds Alice as an administrator.
- Alice also logs in and creates a new graph called “Catalyst-Repos”.
- Alice then connects the team’s GitHub repos as data sources for the “Catalyst-Repos” graph. She specifies that she wants Kartograph to sync the latest data from their repos every 24 hours.
- Since this is a new graph, Kartograph immediately initiates an extraction job. It fetches the data from the git repos, and the extraction agent begins extracting entities and relationships.
- The initial extraction completes and the data is ingested into the graph by the graph domain.
- At this point, Alice and Bob see that their graph is ready. They copy the command to register the Kartograph MCP server with Claude Code, which gives the agent access to connected context built from their team’s three git repos.